A Primer To DAO
DAOs, or decentralized autonomous organizations, are collectives that leverage blockchains and other technologies to make decisions in a democratic manner.

DAOs, or decentralized autonomous organizations, are collectives that leverage blockchains and other technologies to make decisions in a democratic manner.
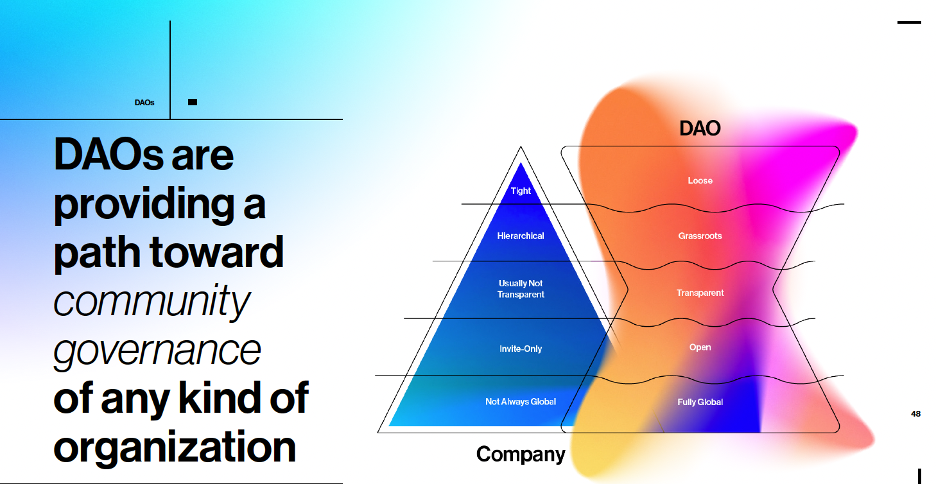
A DAO's goal is to decentralize the operation of firms, nonprofits and other entities by making functional and financial information transparent and allowing token-holding members to propose, vote on and enact changes.
DAOs come in many different shapes and sizes, including ones that govern crypto protocols, make venture investments, provide services to other DAOs, and purchase NFTs.
Beyond the three main principles of decentralization, autonomy, and organization, DAOs are guided by several other principles:
- Transparency: Everything that happens within a DAO is recorded on the blockchain and is accessible to anyone. This openness is fundamental to the trust and collaborative nature of DAOs.
- Democratic Governance: DAOs often operate on democratic principles where every member has a voice. Decisions such as the allocation of resources or strategic directions are made through collective voting.
- Token-based Incentives: DAOs usually have a native token that is used to incentivize participation and align the interests of all members. Tokens can represent voting power or a share in the profits.
- Openness and Inclusivity: Anyone, regardless of their location or status, can join a DAO, contribute, and become a stakeholder. This principle breaks down barriers to entry and promotes diversity and inclusivity.
- Immutable and Programmable Rules: The rules of a DAO are written into smart contracts on the blockchain, ensuring they cannot be changed without consensus and automatically execute once conditions are met.
- Self-Sustainability: DAOs are designed to operate indefinitely without a central authority. They can sustain their operations through member contributions, fundraising, or revenue-generation methods encoded into their smart contracts.
- Interoperability: Many DAOs are built on common standards like Ethereum's ERC-20 or ERC-721, enabling interoperability with other DAOs, dApps, or blockchain platforms.
DAO Landscape
- According to analytics firm DeepDAO, there are more than 4,800 DAOs in operation with ~$8.3 billion in treasuries.
- In 2016, a DAO known as “The DAO” raised $150 million in ether to create an organization for collective investment in blockchain projects.
- 17,000 members of Constitution DAO raised $47 million and tried to buy one of 13 surviving original copies of the U.S. Constitution.
- AssangeDAO raised over $53 million to bid on an NFT that would support the release of WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange.
- The LinksDAO sold out of memberships and raised more than $11 million in its quest to buy a real-world golf course.
- A crypto investment DAO called dao5 has launched a $125 million fund.
- Infrastructure companies that provide DAOs with tools to launch and grow have collectively raised more than $100 million in recent months.


